
Dressings and splints are critical
to protecting INTEGRA® Template sites, however, extra
care must be taken to avoid shearing and dislodgement when
moving the patient. Shearing can result in the formation
of hematomas, fluid accumulation, and ultimately, infection.
The techniques deployed in positioning and moving the
patient may help to reduce the chance that this mechanical
dislodgement will occur when the patient is transported
or positioned. It is important to plan your strategy for
moving the patient ahead of time, ensure that you have
sufficient help to move the patient.
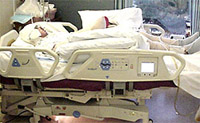
Specialty
Beds can be an important tool in caring
for the INTEGRA® Template patient. These beds,
generically known as intermittent zero pressure or
air fluidized specialty beds, have low air loss mattresses
designed to maintain appropriate core
body temperatures. Additionally, they are adjustable,
compensating for the prone or supine patient. Care
should be taken to ensure that the patient is appropriately
dressed and bolstered while manipulating the bed. |
 |
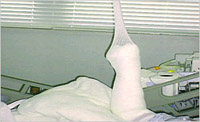
| Elevation
of Appendages. The occurrence of edemas is
not uncommon in burn patients. Left unattended, edemas
may lead to excessive fluid accumulation and infection
in INTEGRA® Template patients. Elevating arms and legs
may help in reducing edema. Elevate the appendage
to decrease edema by suspending the limb by the stretch
net, bulky dressing, or padded elbow from an IV tree.
Care should be taken to ensure that excessive stress
is not placed on INTEGRA® Template sites as a result
of this technique. |
 |


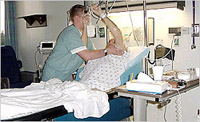
| Walkers
and Other Self-Assistance Devices. Most of
these devices are common sense driven. Your physical
therapist may be able to suggest alternative modifications
to existing ambulatory devices that will better fit
your patient's needs. Generally, devices that allow
you to keep your hands off the patient are ideal.
If patients are able to ambulate, helping them do
so may help speed their recovery. There are a variety
of walkers that allow patients to bear weight on their
arms and not on their INTEGRA® Template sites.
They alleviate the need to hold patients by their
arms and can actually enable them to ambulate on their
own. Self-assistance, "monkey bars," and
overhead bars that allow patients to pull themselves
up will help you move and position the patients. |
 |


|
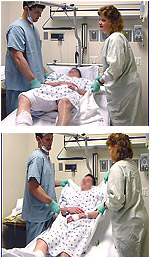
Re-Positioning
the Patient (Straight Lift with Sheet).
It is easy to make a mistake and try to move the
patient by grabbing an INTEGRA® Template site.
If you grab a patient under
the arms and drag them across the bed, you will
risk shearing the INTEGRA® Template sites,
particularly on the patient's back, buttocks,
or legs. Use a straight lift with a sheet or blanket
under the patient. Use enough manpower to adequately
lift the patient comfortably.
|
 |